Database Availability Group in Exchange 2010 – Installation Guide
admin | July 12th, 2014 | Exchange Server
Table of Contents:
- Exchange 2010 Database Availability Group
- Exchange Server 2010 DAG Quorum Concept
- Continuous Replication Modes Exchange 2010
- How to Create Database Availability Group
High Data Availability Techniques in Exchange: A Flashback!
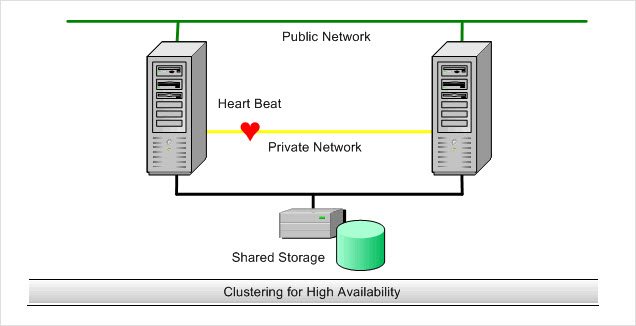
Before Exchange 2007 was launched by Microsoft, there was only one name known for high availability in Exchange and that was Windows Failover Clustering. In Exchange editions (2003 or below), users take advantage of Microsoft Cluster Services (MSCS) where if active node goes down, the cluster failover to passive node and thus users within an enterprise can continue to work without being known with the fact that something has happened. However, it provided protection only at hardware level as single storage subsystem was shared by all the nodes.
For achieving redundancy, enterprises switched to third-party replication services but they were not typically supported BY Microsoft and were out of the budget for some organization. This is when Microsoft realized that for high availability, better native solutions should be provided to users and this came to an end with launch of Exchange 2007 edition. Replication services like Local Continuous Replication (LCR) for small enterprises, Cluster ContinuousReplication (CCR) for medium and large sized enterprises. Later, with launch of Exchange 2007 SP1, Standby Continuous Replication (SCR)was introduced that suited all size structure of enterprises. In case of continuous replication, log files from active Server storage is copied to passive database where it is replayed.
Local Continuous Replication saved the copy of storage group on local volume to mailbox Server which made it a failure in providing redundancy.
Cluster Continuous Replication was a huge success because it provided hardware and storage level redundancy thus providing foolproof high availability solution to users through asynchronous replication technology. However, since it was not developed with site-resiliency concept in mind and thus CCR for multi-site was not a convenient solution.
Standby Continuous Replication made it possible to ship log files to Exchange 2007 Server mailbox role. Since it was free from Windows Failover Clustering concept, the log files from clustered as well as non-clustered mailbox can be carried to another Server. Also, there was provision to lag log files to active Server for seven days so that in this time period if anything goes wrong, it is fixed and is then moved to Server having passive copy.
Exchange 2010 Database Availability Group
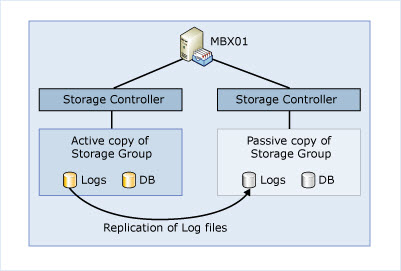
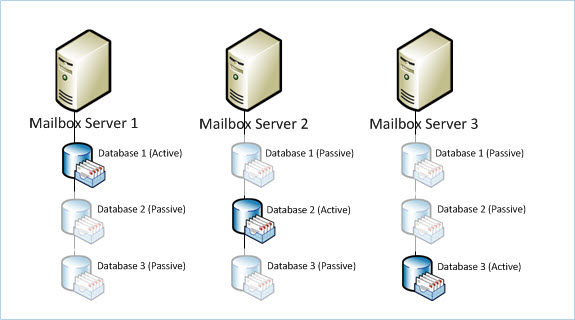
Database Availability Group is the combination of multiple mailbox Servers (maximum of 16) where a copy of active database is shared with passive database. There is only one active database and there can be one or more passive databases that are installed on Servers with mailbox server role installed. Log files of active database are synced with passive copy of database. Although Windows Failover Clustering is the basis of DAG but in spite of failover to passive node the database failover to another DAG member.
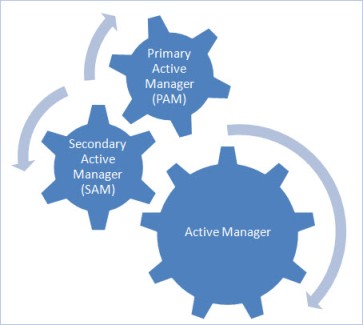
In Exchange 2010, SCR and CCR have been combined to give better high availability framework which is known as Database Availability Group (DAG). Unlike Exchange 2007, the main component of DAG is Active Manager was used for failover and switchover management in spite of Exchange cluster resource DLL. Active Manager in of two types:
Notable Facts about DAG Exchange 2010
Less Reliance on Windows Failover Clustering: DAG uses some of the components of WFC like heartbeat, cluster database, and file share database. Because of this, it is mandatory that Exchange 2010 DAG is installed only on Windows 2008 SP2 or R2 enterprise edition.
Existence of One or More Server Role: When Cluster Continuous Replication is used separately, a Server can only have mailbox server role installed on it. However, with DAG there is freedom to install more than one Server role.
Manage DAG through Exchange Tools: For managing CCR services, cluster management tools were used while DAG can be managed by using Exchange management tools like EMC.
DAG can have 16 Mailbox Servers: A maximum of 16 members can be part of Exchange 2010 Database Availability Group which means there can be 10 copies of a database available. Standard edition of Exchange 2010 can have 5 databases on a mailbox Server. However, this limit extends for enterprise edition where there can be 50-100 databases per Server.
Less Switchover and Failover Time: In DAG Exchange 2010, the failovers and switchover takes place within 30 seconds which was earlier few minutes.
Exchange Server 2010 DAG Quorum Concept
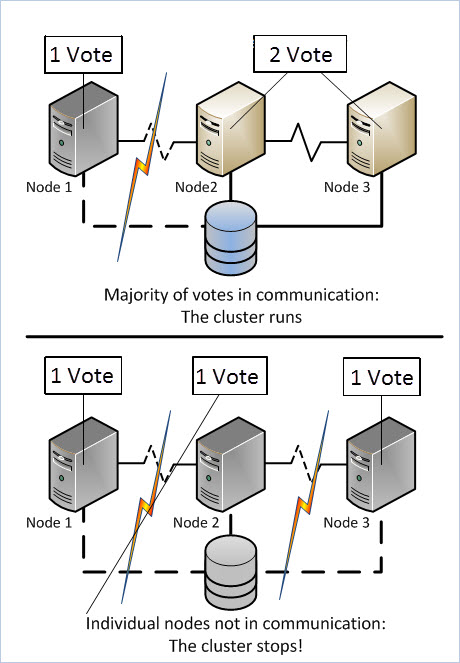
As we discussed before that DAG uses Windows Failover Clustering to some extent, it follows the Quorum concept too. If this is new to you, then just consider it like a voting process where one wins only when it has majority of votes available. In case of DAG, it means that odd number of mailbox Servers should be available so that it can be decided as which member of DAG should be triggered when active database goes down. If there is even number of members in DAG, then not any of them is capable to make decision as which one will be the active copy of database. In that case, an additional Server called File Share Witness will help which is Hub Transport Server in most of the cases.
Continuous Replication Modes Exchange 2010
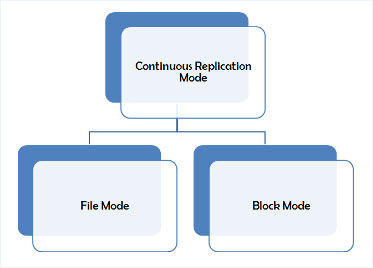
Database between DAG members is copied through continuous replication technique which is further divided into: File Mode Replication and Block Mode Replication. Here is a brief introduction on both these replication types:
File Mode Replication: Standard size of a log file in Exchange 2010 is 1MB. When this replication mode is used, a log file is first filled and then it is synced to the passive copy of database. This kind of replication services works absolutely well but have a limitation that log file will not be shipped to passive database until it is fully filled. This means if a failure happens in between, the changes and up-dations in active database will not be reflected to passive database.
Block Mode Replication: In this replication mode, once a transaction is complete and written to the log file, it is shipped to log buffer of passive database. When log buffer is full, a log file is build and replayed. This proves extremely helpful in scenarios if active database fails because the most updated copy of database will be available through passive copy.
How to Create Database Availability Group
Exchange 2010 DAG can be created either using the GUI management tool (EMC) or command-line interface (PowerShell cmdlets). Once DAG environment is created, mailbox Servers are added to them for redundancy. Since a lot of bandwidth is being consumed while replication, it is suggested to have an individual network for DAG for the purpose of load balancing.
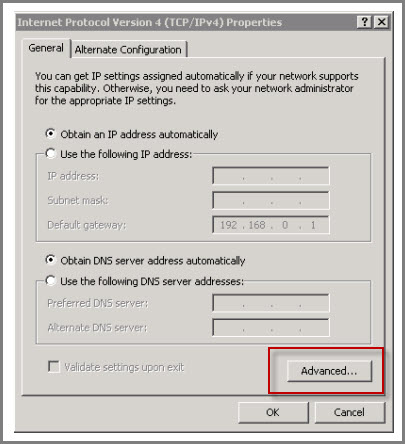
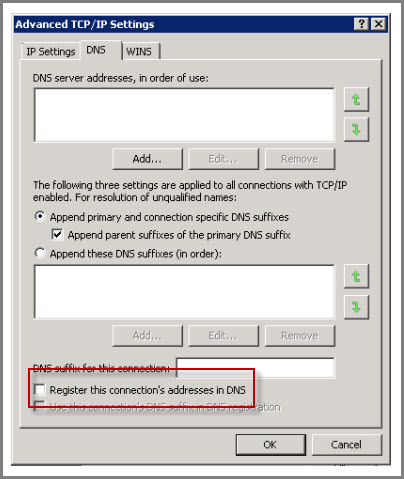
Important to Note: Make it a point that every database in the enterprise have a unique name. In the above environment, the Servers are configured with two interfaces (primary and secondary) it is mandatory that the secondary interface do not enroll itself has the Domain Name Server. To ensure this, following steps have to be made: For secondary interface, open “TCP/IPv4 Properties” and click on the “Advanced” button.
Click on the “DNS” tab and navigate to “Register this connection’s address in DNS” option and disable it.
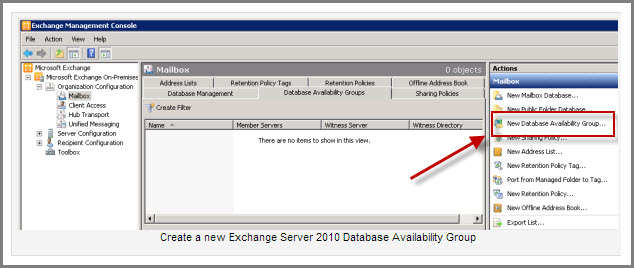
Open EMC and in the console tree, click on “Organization Config/Mailbox”. In the actions pane, click on “New Database Availability Group”
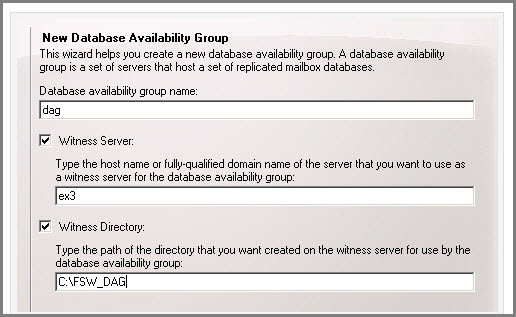
In the window that pops up, enter name of DAG, Witness Server, and the file path for Witness Server.
Click on “New” button and then hit the “Finish” button to exit the wizard.
Add Mailbox Server to DAG
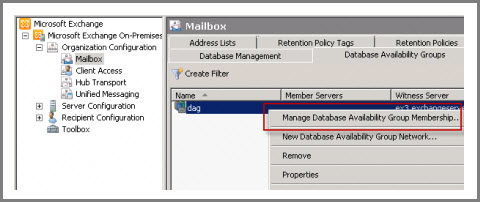
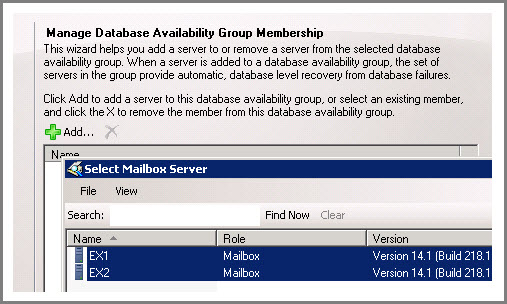
Open EMC, select DAG into which database has to be added. Right click on it and select “Manage Database Availability Group Membership”.
To select DAG member databases, click on “Add” button.
Configure DAG Networking
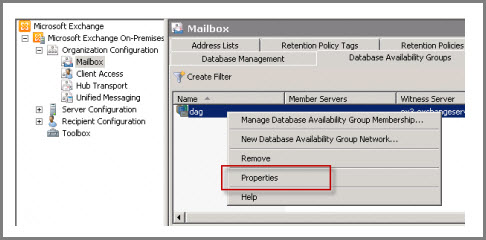
Right-click on the DAG and click on “Properties”
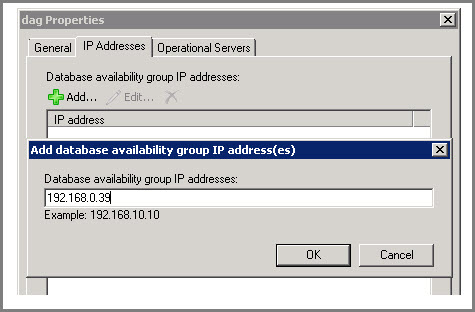
Click on “IP Address” tab and provide a static IP for DAG by clicking on “Add” button.
Add Mailbox Database to DAG Exchange 2010
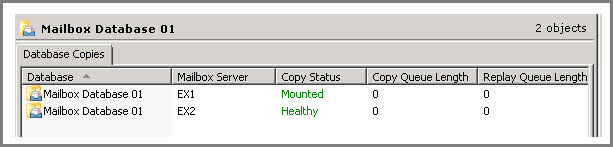
Now after adding Servers to DAG, it is the time to add mailbox databases to them. Open EMC and move to “Database Management” tab in the result pane. A list of mailbox databases will be enlisted in the result pane. Right click on the database and choose “Add Mailbox Database Copy” 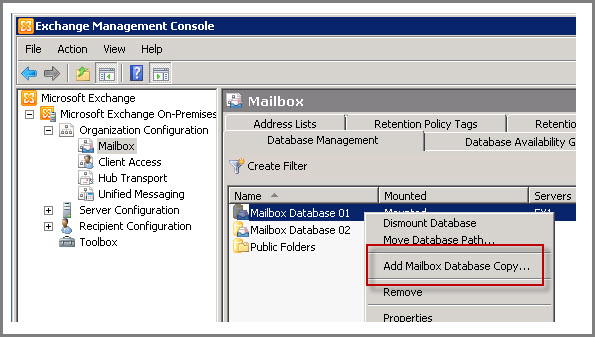
To select DAG Server for the database, click on “Browse” button. Click on “Add” button and repeat the process for number of mailboxes that you wish to add to DAG Servers.
Summary: In this segment, we went through the history of high availability solutions in Exchange and how introduction to DAG made a difference. Also, a discussion on DAG Quorum, log replication modes is done along with step-by-step guidance for how to create Database Availability Group in Exchange 2010.